How to Use Google Analytics Site Search Reports
If your website has a search bar, you need to ensure you’re making the most of this valuable report in Google Analytics. It’s quick to set up and can soon be giving you all sorts of insights and ideas that you may never have had without it.
The Site Search report is found under Behavior and is focused on recording how people interact with the search functionality on your website. This is actually even more valuable since organic keywords started appearing as “(not provided)”, as this report shows what people have actually typed, even if it is on your site instead of into Google – it’s likely that there are overlaps!
Setting Up Site Search Reports
To set this report up, navigate to the Admin, then the View Settings for your chosen profile and scroll down to the Site Search Settings section. Here you just click the button to turn it on and then type or paste in the query that your website uses in search parameters. For example, searching on this site gives you a results URL that looks like this:
http://searchenginewatch.com/search?q=analytics
In this example, the “q” is the search parameter, so this is what would go in the field here:
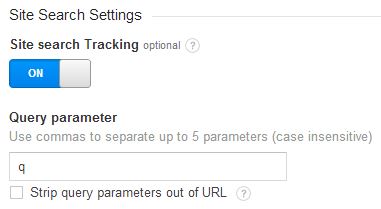
You will find a tick box under this option which gives you the choice to strip parameters out of the URL. If that was ticked for Search Engine Watch all search results URLs would show in the content reports under /search, whereas without ticking it each search will generate a URL with the query included, which will break out the results and not allow you to see the data for search results pages in one row in the content report.
There are benefits to both methods, so it will depend on your reporting and website setup as to which choice will work best for you.
To get an even more detailed breakdown of data in the reports you can also specify categories, if that applies to your website. Here you pop in each category parameter and you will have a report available to group activity together within these.
Site Search Reports
The Overview report, much like any other, gives you a summary of the data relevant to that report. In this case it gives you a clear percentage of how many visits on your website included the use of the search functionality as well as how the interaction played out following the search.
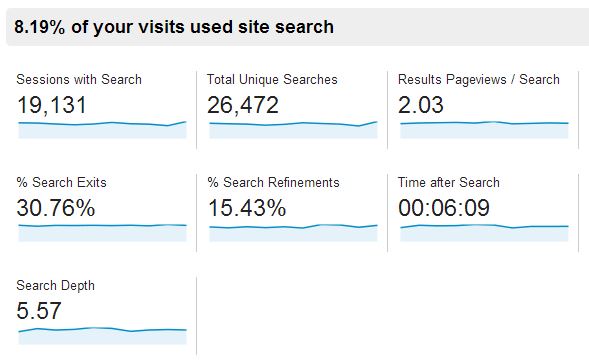
Usage
This report has two rows of data, one for visits with site search and one for visits which did not include the use of the search functionality. This allows you to directly compare the success rate of people using search against those who don’t to work out whether the conversion rates are very different, whether new visitors are more likely to be using the search box, or how much revenue you have generated by people using this option.
All standard metrics are available and the Site Usage, Goals, and E-Commerce reports are easily accessible above the graph so you can drill into the most relevant report for your site.
Search Terms:
This is where it gets very interesting! The words and phrases that your visitors have used in your search box are recorded here so that you can work out what people are looking for on your website. Each query used is shown alongside search usage metrics but Goal and E-Commerce reports are also available.
There are many uses for this report. Some examples include:
- How many pages it took for people to find what they wanted
- How many visitors gave up and left the website
- Which keywords did not have good enough results so users had to refine their terms
- How persistent visitors were with their query, by how many pages of results they looked through
- Most common queries
- Trends and identifying new searches which can help you identify products to stock or content to write about
- Identifying common misspellings or other ways to phrase something
- Which areas of the site people choose to search for over navigating through a menu for
- Which queries lead to users being engaged with the website
- Queries that have good conversion rates
As mentioned above, this data can also be broken down by category, so if you have set this up, click the link above the data table for “Site Search Category” and you will be able to see this data.
Pages
The Pages report in this area is all about which pages of the website the user was on when they made the search. If you see (entrance) under this report, your visitors are entering the website on a search results page, which may be caused by marketing activity or natural search results using search URLs.
Sometimes the Pages report can be useful for working out which pages are the ones on which visitors give up on using the navigation and switch to a different method of using the website.
Clicking the “Destination Page” link above the data takes you to a report showing where users went on the website following a search.
Useful Tips
If you have the opportunity to do so, I encourage you to set this tracking up for your website. It’s your prerogative to know what’s going on within your website and what it is that people want or cannot find.
Here are some extra ideas to take away for this area in Google Analytics:
- International Comparisons: It is interesting to see the take-up of search functionality on websites around the world. The percentage of visits with search can vary dramatically from country to country, so do ensure you focus on the most suitable website navigation methods for your users.
- Language Use Globally: Also on the topic of international data, when you have a website specific to another country or language, you will benefit from keeping a close eye on the language used in search queries, as this can help you identify hard-to-translate items that people cannot find or terms that you can use an English version for as it may be more widely used than a local language.
- Internal Campaign Tracking: An out-of-the-box idea for tracking internal banners by Justin Cutroni is to tag them with parameters that you can analyze in search reports instead of resorting to using campaign tracking tags on internal links, which is not recommended.
Top 5 Mistakes to Avoid When Using Google Analytics with Site Search
There is a wealth of information in Google Analytics, helping website owners gain a deeper understanding of who’s visiting their site and how often; what they click on and their navigation path; and what pages or links lead to particular outcomes like downloads or purchases. Google Analytics shows how effective site search is in generating clickthroughs and conversions, shopping cart abandonment rates and more.
However, without knowing how to interpret the data and what it’s telling you, you’re not getting the whole picture. For example, you might put too much attention on raw totals, when it makes more sense to look for trends or compare different segments of data. Or, you might inadvertently exclude traffic that you should keep measuring.
The engineers I work with have developed a useful list of common mistakes that website owners make when using Google Analytics and site search, along with guidance for better understanding of what’s happening on your site.
Mistake #1: Trusting that your site search statistics are correct.
By default, Google Analytics tracks every page against the URL of the page loaded. Assuming that your search page has the URL “http://sub.domain.com/search?w=keyword” Google Analytics tracks the page as “/search?w=keyword.”
By default, Google Analytics tracks every page against the URL of the page loaded. Assuming that your search page has the URL “http://sub.domain.com/search?w=keyword” Google Analytics tracks the page as “/search?w=keyword.”
When setting up site search reporting, you specify the query parameter that defines a search page view. In the above case, the query parameter value would be “w.” This means that any URL on your site that contains the query parameter “w=xyz” will be tagged as a site search page view.
The problem here is that this query parameter may exist on non-site search pages. It’s not always easy to see that these pages exist. There could be non-site search pages that have this query parameter in the URL – which means site search reports may not be accurate, and you will not get a clear picture of how site search is performing.
The solution is to use advanced segments instead, since they’ll allow you to be more specific about the site search segmentation and will give you the platform to be more precise about identifying visits with a site search page view. For example, you can say something like: “Include pages that begin with /search” or “Include pages that contain the query parameter w.”
It’s also a good idea to avoid using site search URLs in your navigation and/or PPC campaigns. Get a different URL structure for the same page setup, such as http://sub.domain.com/ppc/keyword or http://sub.domain.com/nav/brand/nike/0.
Mistake #2: Focusing on the totals. Google Analytics will always under report results, given that it is focused on JavaScript tracking. Therefore, results don’t take into account that there is a small percentage of site visitors who will click away before allowing the page to load long enough for the tracking code to fire. There are also site visitors who will have JavaScript and/or cookies disabled.
Thus, you shouldn’t be too concerned with exact results. Instead, focus on trends and comparing different segments of data (e.g. visits with site search versus visits without site search) or time periods (e.g. visits with search in June compared to July).
Mistake #3: Forgetting about AJAX. The AJAX programming language has become ubiquitous on the web in recent years, since it allows site visitors to load content without reloading an entire web page. You’ll often see AJAX used for search results so that users can quickly access more results without waiting for new pages to load.
Before the widespread use of AJAX, if a user wanted to click on a new page of results or perhaps select different refinements, the page would have to be loaded again and the Google Analytics code would have tracked it as another page view. But with AJAX, these interactions on your site are no longer tracked. It has become common to use virtual page views or event tracking depending on what you are trying to track.
Source: searchenginewatch.com/
moz.com
moz.com








